
PID (or “photoionisation detector”.) detection uses ultraviolet light to ionise VOC molecules in order to measure a resulting electric current. This simple method allows PIDs to detect VOCs at ultra-low levels, from parts per billion (ppb) to parts per million (ppm).
Most industry insiders know that volatile organic compounds (VOCs) evaporate rapidly when emitted into the air, react with other gases, and form other air pollutants. Exposure to them can result in serious health issues and in the long term, damage the local environment.
 Many VOCs are human-made chemicals. They are mainly used (or produced) in manufacturing paints, pharmaceuticals, and refrigerants.
Many VOCs are human-made chemicals. They are mainly used (or produced) in manufacturing paints, pharmaceuticals, and refrigerants.
Additionally, the petrochemical industry produces and uses many VOCs, such as crude oil, gasoline, diesel, and plastics.
Like most other industrial gases and chemicals, VOCs can leak from pipes, tanks, valves and other critical equipment. This can result in immediate danger to life and at the very least, regulatory compliance issues for your organisation.
Using PID in the Petrochemical Industry
Advantages
PID detection is much faster, more sensitive, portable, and more versatile. It allows the detection of VOC at low levels in a variety of environments.
PID detection is used in the petrochemical industry to:
- Monitor worker exposure to VOCs and ensure compliance with occupational health and safety standards.
- Optimise the production process and reduce waste and emissions.
- Detect leaks, spills, or emissions of VOCs from all main equipment.
- Comply with local and international regulations and standards.
Limitations
Like anything else, PID detection does come with its limitations. Factors such as humidity, temperature, pressure, and interference from other gases can affect the accuracy of PID detection. Because of this, it is crucial that regular calibration and maintenance are performed to ensure reliability and precision.
When choosing a PID detector, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Range and resolution of the detector.
- Type and intensity of the UV lamp.
- Response time and recovery time of the detector.
- Battery life and power supply of the detector.
- Size and weight of the detector.
- Ease of use and display of the detector.
- Data logging and communication capabilities of the detector.
- Durability and resistance of the detector to harsh conditions.
- Cost and availability of the detector.
Conclusion
It’s fair to say that PID detection is a reliable and versatile method for monitoring VOCs in the petrochemical industry. By understanding both the benefits and limitations of PID detection, you can choose the correct equipment for your needs, ensuring the safety of your workers, the environment, and your business.
Rockall Safety PID Solution
Rae Systems UltraRAE 3000 Benzene Detector
The UltraRAE 3000 is the most advanced Compound-Specific Monitor on the market. Its Photoionisation Detector’s (PID) extended range of 0.01 to 10,000 ppm in VOC mode and 10 ppb to 200 ppm in benzene-specific mode makes it an ideal instrument for applications from entry pre-screening during refinery and plant maintenance to hazardous material response, marine spill response and refinery down-stream monitoring.
Inexpensive analysis using low-cost RAE-Sep tubes vs gas detection tube; less expensive than a portable GC, and no annual factory calibration is required.
Rae Systems MiniRAE 3000 Gas Monitor (PGM-7320)
Ideally suited for a range of industrial applications, the Rae Systems MiniRAE 3000 Monitor is one of the most advanced portable VOC monitors available on the market.
This handheld VOC monitor features a large backlit LCD screen with easy operation via the use of glove-friendly buttons. Datalogging capabilities are included, offering up to six months storage.
It features a robust housing that is suitable for use in harsh conditions, and comes with an integrated sample pump for drawing up to 100 feet.
Rae Systems MiniRAE Lite
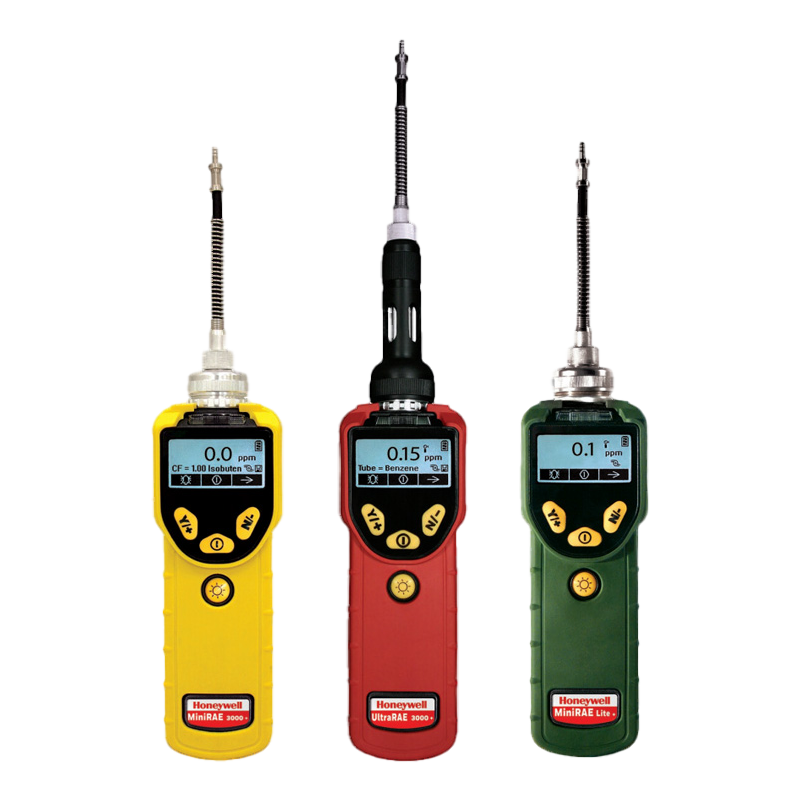 Ideally suited for leak detection and environmental cleanup, the Rae Systems MiniRAE Lite is a reliable hand-held VOC monitor.
Ideally suited for leak detection and environmental cleanup, the Rae Systems MiniRAE Lite is a reliable hand-held VOC monitor.
With a photoionisation detector’s (PID) range of 0 to 5,000 ppm, this device can be used for various applications. It comes with a rugged casing that protects it from hazards in harsh environments.
The pump can draw a sample up to 100 feet away and has a 3-second response time.
For further questions about PID detection or to learn more about our products and services, contact Rockall Safety at 02920 759 683. Our qualified team will be happy to help you find the right choice for your needs.
Written by Emma Curthoys

